PhD in biology or biological science is designed to provide advanced knowledge in the field of biology and related interdisciplinary subjects like ecology, genetics, microbiology, cell biology and molecular biology, etc to students through research.
Biology is a subject to study life, including the study of animals, plants, microorganisms, cells and related things. It is one of the most popular subjects among students due to vast research opportunities.
Molecular biology, cell biology, genetic and microbiology like subjects are now very much in demand. Universities offer different types of doctorate courses in pure and applied biological science subjects.
Based on the interest of students, they can choose their own study field and can do excellent research. A candidate with a PhD in biology can earn higher than a doctorate in another field.
In the present article, We will explain to you the entire process of getting a PhD degree in any subject of biology.
Related article: What is PhD?- History, Definition, Origin, Requirement, Fees, Duration and Process.
Admission process:
To be eligible for doing a PhD in biology or biological science one should have a master’s degree or post-graduate degree in biology, biological science or related interdisciplinary subjects.
Minimum of 55% mark of 5.3 GPA (in USA) in the overall masters degree is compulsory to apply for the same.
M Phil after the master’s degree is also taken into account for admission procedure. Some universities allow the M Phil student to directly appear in the interview without the entrance exam.
However, for other students, after completion of master degree, the entrance exam is compulsory, it is conducted by either university itself or by the central body.
Note that some universities in the USA and UK directly allow students in the PhD interview without taking an external examination. Their research background is preliminarily considered during the interview.
A good score in IELTS, TOEFL and GRE is required for foreign students.
Process of admission:
Usually the process of PhD admission is streamlined by universities.
First, apply online through the official website of the university following the notification.
Upload all the documents (enlisted elsewhere in this document) while filling the form. Download the hall ticket.
Appear in the entrance exam on the given date with the hall ticket if applicable.
After clearing the entrance exam, you have to appear in the personal interview during which the candidate has to verify all their original documents and submit the research proposal.
A research proposal must include the problem, method to evaluate the problem, general introduction and other related information in a 10 to 12 pages.
In the next stage of admission students have to select their research guide or supervisor under whose supervision they have to complete their PhD.
After completing all these steps, at the end of the first year, a candidate has to clear the course work examination, compulsorily in order to continue PhD.
Steps in admission:
- Follow the notification
- Apply online
- Upload all documents
- Download hall ticket or form.
- Appear in the entrance exam if applicable
- Choosing the PhD guide
- Appearing in the PhD interview
- Document verification
- Clearing the course
Documents required:
- Undergraduate and postgraduate degree certificate and marksheets
- Living certificate
- Result of clearing entrance examples like NET, GATE, JAM or JEST.
- University transcription
- IELTS, TOEFL or GRE marksheet if needed.
- Research proposal
- Recommendation letter from the guide
- Student consent letter
- Other related documents
PhD in biology: duration
Usually as per the university rules and regulation, a candidate has to pass a minimum of 3 years during their PhD tenure to complete the research. Although it may take longer.
PhD in biology takes 4 to 7 years to complete the research. For some extensive finding it may take up to 10 years, there is no time bound for that. However, a student has to justify their progress every semester.
PhD in biology or related subjects takes more time to complete in comparison with other subjects. The reason is extensive lab work. A candidate has to do lab work, perform trial and error experiments, check protocols and SOPs to even start their work.
Also he or she has to do wet lab work as well as dry lab work too. Doing a PhD in biology or biological science it’s tedious process and takes more time.
Read more:
PhD in biology subject and syllabus:
Biology is a huge subject with so many subfields and applied subjects. Here I am enrolled in some of the popular subjects and courses for doctorate in biology and its entire syllabus.
| Subject | Syllabus |
| Pure botany | Plant biology, plant developmental study, Anatomy, plant ecology, plant systematics and evolution, plant physiology, Plant genetics, Plant metabolism, plant biotechnology and economical importance of plant. |
| Zoology | Animal classification, evolution, migration, Animal metabolism and development, animal genetics, Animal behavior, biodiversity, Molecular biology, Immunology, Applied zoology, parasitology and animal histology., Animal physiology and biochemistry. |
| Biotechnology | Cell biology, genetics, Biochemistry, Microbial biotechnology, Bioinformatics, Agri Biotechnology, Medical biotechnology, Enzyme technology, Food biotechnology, Plant and animal biotechnology and Environmental biotechnology |
| Microbiology | Microbial genetics, microbial techniques, biochemistry, virology, bacteriology, Environmental microbiology, Pharmaceutical microbiology, Enzymology |
| Genetics | Genetic techniques, molecular genetics, evolutionary genetics, medical genetics, animal and plant genetics, cytogenetics, metagenomics and environmental genetics. |
| Environmental science | Fundamentals of Environmental Science, Environmental Biology, Environmental chemistry, Environmental pollution control, Environmental biotechnology, Environment and human health, Solid waste management. |
| Ecology | Ecology and Environmental science, ecology and statistics, Terrestrial Ecology, Aquatic ecology, plant ecology, animal ecology, conservation biology, ecology and evolution, industrial ecology, |
| Mycology | Introduction to mycology and fungi, fungal classification, economical importance of fungi, toxic and fungi, genetics of fungi. |
| Conservation biology | Biodiversity and conservation, Distribution of biodiversity, conservation biology and ethics, conservation management, agriculture and conservation, climate adaptation planning and policy. |
| Evolutionary biology | Concept of evolution and origin of life, Origin of prokaryotes and Eukaryotes, theories of evolution, Evidence of evolution Source of variations and evolution, Microevolution concept and sources, Phylogenetic tree |
| Bioinformatics | Introduction to bioinformatics, genetics and biotechnology, introduction to NCBI & EMBL, amino acid and protein synthesis, designing molecules and proteins. |
| Molecular cell biology biology | Enzymes and proteins, cell cycles, cell division, replication and transcription, pathways for synthesis of biomolecules, Apoptosis and cell organelles. |
| Cell biology | Cell cycle, cell synthesis, cell death and apoptosis, cell organelles, biosynthesis pathways, inheritance of genetic material and cell metabolism. |
| Cancer biology | Introduction to cancer, cancer causing agents, cancer and genetics, ongogenes, protooncogens, carcinogens, types of cancer, cancer treatment and therapies. |
| Endocrinology | Introduction and principle to endocrinology, hormone action, molecular biology, receptor biology, clinical endocrinology, hormone action and metabolism, various glands and secretion of hormones, Neuroendocrinology and endocrine disorders, Endocrinology and pregnancy. |
| Immunology | Introduction to immune system, antigen and antibody, antibody genes and generation of diversity, antigen-antibody reaction, histocompatibility complex, autoimmune disorders, Maturation of T cell and B cell, Immune response to infection, transplantation and immune system, cancer and immune system. |
| Hematology | Introduction to Hematology, types of tissue, blood and component of blood, type of blood cells, RBC and WBC maturation, cell death, blood disorders, genetics of blood disorder, dianostic techniques. |
| Agriculture | Overview of agriculture, agri-genetics, agri-biotechnology, plant hybridization methods, backcross and test cross, economically important plants, GMO and plant tissue culture. |
PhD in biology jobs and opportunities
Biology is the biggest and popular science field. Students with PhD in biology have so many job and career opportunities, thousands of job opportunities are there at their door stop.
A doctor of philosophy in biology can go for academics and become a professor, dean or head of the college of university. Meanwhile they can also continue their research there.
Furthermore, they have numerous research opportunities in bacteriology, virology, genetics, microbiology, environmental science, marine science, plant research, animal research, biotechnology research centre or related disciplines.
A good candidate can be absorbed by a research centre and research companies immediately. Geneticist, psychologist, cytogeneticist or microbiologist can become a medical professional too.
Note that, higher positions in organisations, research centre, colleges or in companies the higher positions are reserved for doctorate of philosophy only.

PhD biology salary and income
As the PhD is the highest level of esteem, the rewards and earning potential is also very high for PhD candidates. Commonly a PhD degree holder can earn 50,000$ to 5,00,000$ per annum or even more.
Some expert scientists can even earn millions. Also, with a private business or startup or through royalty they can earn a decent amount of money every year.
| Top PhD courses | Earning per year in $ |
| PhD in biology | $90,000 to $1,15,000 |
| PhD in microbiology | $75,000 |
| PhD in biotechnology | $79,000 to $82,000 |
| PhD in genetics | $50,000 to $1,00,000 |
| PhD in environmental science | $70,000 |
| PhDin botany | $48,000 to $55,000 |
| PhD in marine biology | $50,000 to $79,000 |
| PhD in animal husbandry and zoology or animal behaviour | $63,000 to $1,01,850 |
| PhD cell and molecular biology | $47,000 to $90,000 |
| PhD in agri-biotechnology | $39,000 to $84,000 |
Note that as the expertise and experience increases the salary level also increases. In addition to this, one can also earn with the royalty of their findings, paper or any other intellectual properties throughout their life.
Related article: Doing Online PhD- Advantages and Disadvantages.
Top 20 universities for PhD in biology
| University | Location |
| Harvard university | United States |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology | United states |
| University of cambridge | England |
| Stanford University | United states |
| University of Oxford | England |
| University of California, Berkeley | United states |
| ETH Zurich- Swiss Federal Institute of Technology | Switzerland |
| Yale university | United States |
| California University of Technology | United States |
| University of California, Los Angeles | United States |
| University of California, San Diego | United States |
| Cornell University | United States |
| Imperial College of London | England |
| University of Toronto | United States |
| University of Tokyo | Japan |
| National University of Singapore | Singapore |
| University of California, San francisco | United States |
| Columbia University | United States |
| The University of Edinburgh | England |
Top Universities for doing PhD in Biology in USA:
| University | Location in USA |
| Harvard university | Cambridge, MA, United States |
| Massachusetts Institute of Technology | Massachusetts, United states |
| Stanford University | Northern California, United states |
| University of California, Berkeley | Berkeley, United states |
| Yale university | New Haven, United States |
| California University of Technology | California Blvd, United States |
| University of California, Los Angeles | Los Angeles, United States |
| University of California, San Diego | San Diego, United States |
| University of California, San francisco | San francisco, United States |
| Columbia University | New York, United States |
Top Universities for doing PhD in Biology in India:
| University | Location |
| Indian Institute of science, Bengaluru | Bengaluru, India |
| Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi | New Delhi, India |
| All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi. | New Delhi, India |
| Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi | New Delhi, India |
| University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad | Hyderabad, India |
| Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani | Pilani, India |
| Delhi University, New Delhi | New Delhi, India |
| Calcutta University, Kolkata | Kolkata India. |
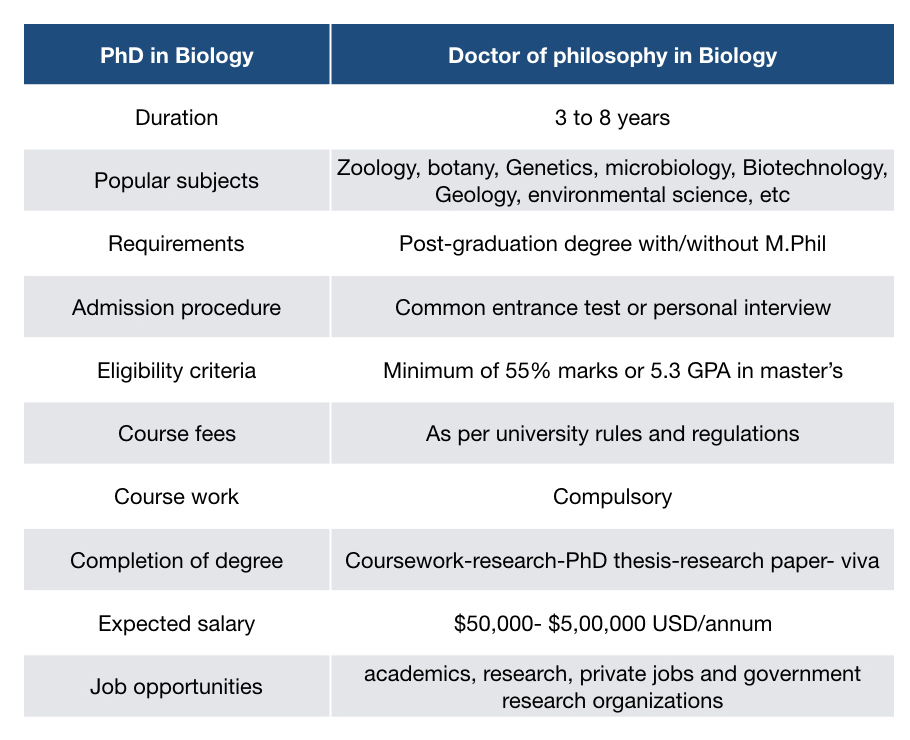
Summary of the article:
| PhD in Biology | Doctor of philosophy in Biology |
| Duration | 3 to 8 years or more |
| Popular subjects | Zoology, botany, Genetics, Microbiology, Biotechnology, Geology, environmental science, cell biology, molecular biology and biochemistry. |
| Requirements | Post-graduation degree with/without M.Phil |
| Admission procedure | Common entrance test or personal interview |
| Eligibility criteria | Minimum of 55% marks or 5.3 GPA in master’s |
| Course fees | As per university rules and regulations |
| Course work | Compulsory |
| Completion of degree | Coursework-research-PhD thesis-research paper- viva |
| Expected salary | $50,000- $5,00,000 USD/annum |
| Job opportunities | Academics, research, private jobs and government research organizations |
Final words:
If you are a student of science and want to pursue your career in biology, go for it. There are numerous research activities going around the world and you can be its part soon.
Biotechnology, microbiology, genetics, molecular cell biology and bioinformatics are the future of biology. Soon on the subject and develop outstanding expertise in some technique.




